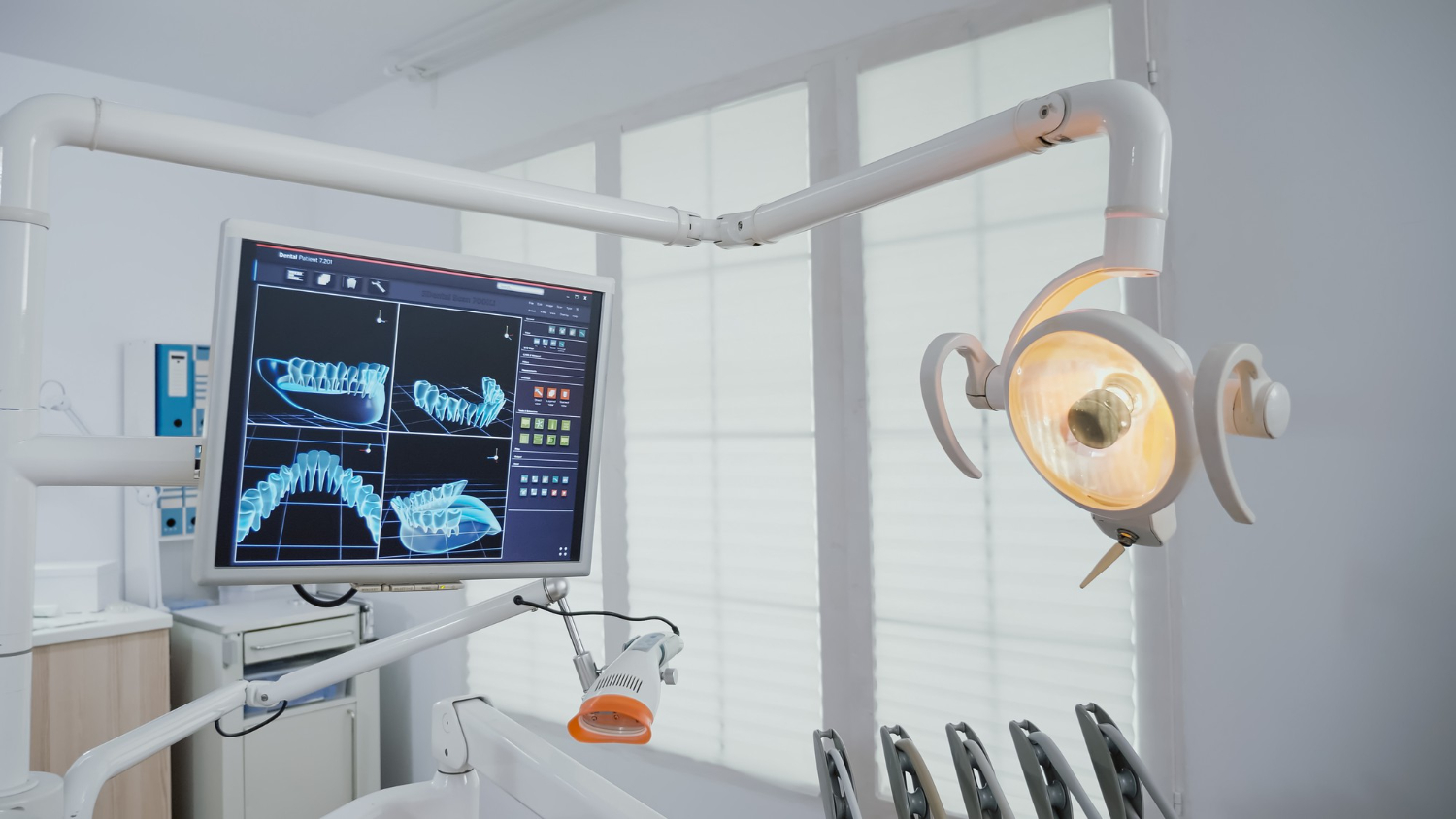
Sirona Cadcam Milling Machine
Sirona Cadcam Milling Machine
The Sirona CADCAM Milling Machine revolutionizes modern dental care by delivering precise, high-quality dental restorations in record time. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we leverage this advanced technology to enhance our prosthodontics in Miyapur services. From crowns and bridges to veneers, the Sirona system ensures exceptional fit, durability, and aesthetics. With its state-of-the-art milling capabilities, we provide custom dental restorations that seamlessly blend with your natural teeth. Trust Vijay Dental Miyapur for cutting-edge prosthodontic solutions that redefine comfort and efficiency. Experience the future of dental care with the Sirona CADCAM advantage!
CAD/CAM dentistry process
CAD/CAM dentistry combines advanced technology with precision to create high-quality dental restorations. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we use this cutting-edge process for prosthodontics in Miyapur, offering seamless and durable solutions like crowns, bridges, and veneers. Digital impressions and precision milling ensure that every custom dental restoration is a perfect fit, enhancing both function and aesthetics. Trust us for efficient, same-day dental restorations tailored to your unique smile

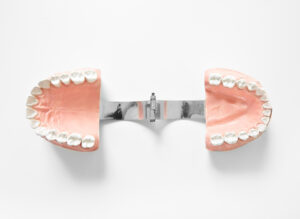
Dental Bridges
Dental Bridges
Dental bridges are a reliable solution for replacing missing teeth, restoring your smile, and maintaining proper oral function. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we specialize in creating high-quality bridges as part of our prosthodontics in Miyapur services. With a focus on custom dental restorations, we ensure each bridge is designed to fit comfortably and look natural.
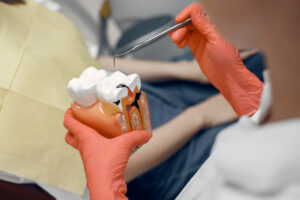
Types of Brides
Traditional Bridges
These are the most common type, consisting of one or more artificial teeth held in place by crowns on adjacent natural teeth.
Cantilever Bridges
Used when only one adjacent tooth is available to support the bridge, ideal for specific situations.
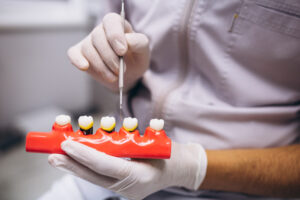
Maryland Bonded Bridges
A conservative option where a framework is bonded to the back of neighboring teeth, requiring less alteration of natural teeth.
Implant-Supported Bridges
These use dental implants for support, offering a durable and permanent solution for multiple missing teeth.
Dental Bridge Procedure
Firstly, the abutment teeth are prepared, which involves recontouring these teeth by removing a portion of enamel to create space for a crown to be placed over it. Then, impressions of the teeth will be made to develop a model from which the bridge, crowns and pontic will be made by a dental lab. Dentists will make a temporary bridge to protect exposed teeth and gums while the bridge is being made. Then, temporary bridge will be removed and the new porcelain or metal bridge will be adjusted to achieve a proper fit.
Benefits of Dental Bridges
Restores Functionality: Enables proper chewing and speaking, improving overall oral function.
Aesthetic Enhancement: Fills gaps in your smile with natural-looking restorations.
Prevents Teeth Shifting: Keeps adjacent teeth in place, avoiding misalignment.
Long-Lasting Results: With proper care, dental bridges can last for years.
Why Choose Vijay Dental Miyapur?
At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we combine expertise and advanced technology to craft custom dental restorations that fit perfectly and look beautiful. Experience the benefits of professional prosthodontics in Miyapur and regain your confident smile with our personalized dental bridge solutions
Dentures
Dentures
Dentures are an excellent solution for individuals who have lost multiple or all of their teeth. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we offer various types of dentures as part of our prosthodontics in Miyapur services. With our expertise in custom dental restorations, we create dentures that are comfortable, functional, and aesthetically pleasing, ensuring that you regain both confidence and comfort in your smile.
Complete Dentures
Complete dentures are designed for individuals who have lost all of their teeth in a specific arch (upper or lower). They are made to fit securely over the gums, providing a full set of teeth that improve speech and chewing functionality.

Partial Dentures
Partial dentures are ideal for patients who have lost only a few teeth. These dentures fill the gaps left by missing teeth and are supported by the remaining natural teeth. They help prevent shifting and maintain the alignment of the teeth.
Implant-Supported Dentures
For added stability and comfort, implant-supported dentures are anchored to dental implants rather than just resting on the gums. This type of denture offers a more secure fit and helps preserve jawbone health.
Flexible Dentures
These dentures are made from a flexible material, offering increased comfort and a more natural fit. They are especially useful for those with sensitive gums or those who prefer a lightweight option.
Care
You need to brush your dentures daily to remove food particles and plaque. Brushing can also help prevent teeth from staining. Rinse your dentures prior to brushing to remove any food or debris.
Try to use a soft bristle toothbrush and a non-abrasive cleanser to brush all the surfaces of the dentures so they don’t get scratched. Clean your mouth properly-including gums, cheeks, tongue and roof of your mouth to remove any plaque. This can reduce the risk of oral irritation and bad breath.
Benefits of Dentures
Restores Function: Dentures improve your ability to chew and speak, restoring the functionality of your mouth.
Aesthetic Appeal: Custom dentures are designed to mimic the appearance of natural teeth, enhancing your smile.
Prevents Jawbone Shrinkage: Dentures help support the structure of your face, preventing the jawbone from shrinking due to tooth loss.
Improved Confidence: With a well-fitting set of dentures, you can smile, speak, and eat with confidence again.
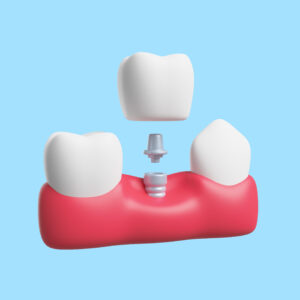
Crowns
Dental Crowns
A dental crown is a custom-made cover that fits over a damaged or weakened tooth to restore its strength, shape, and appearance. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we specialize in providing high-quality crowns as part of our prosthodontics in Miyapur services. Our crowns are carefully designed to meet your specific needs, ensuring optimal function and a natural-looking smile.
Types of Dental Crowns
1. Porcelain Crowns:
Porcelain crowns are a popular choice for those seeking an aesthetic restoration. They are designed to blend seamlessly with natural teeth, making them perfect for front teeth. The material mimics the translucency of natural enamel for an impeccable look.
2. Metal Crowns:
Metal crowns are highly durable and resistant to wear, making them ideal for back teeth where strength is more important than appearance. Common materials for metal crowns include gold and other durable alloys.
3. Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Crowns:
These crowns combine the strength of metal with the cosmetic appeal of porcelain. The metal base provides durability, while the porcelain exterior offers a natural appearance, making them a great option for both front and back teeth.
4. Zirconia Crowns:
Zirconia crowns are incredibly strong, long-lasting, and offer a natural, aesthetic appearance. The material is also biocompatible, making it a great choice for people with sensitive gums or those who need a durable solution.
5. E-Max Crowns:
E-Max crowns are made from a high-quality ceramic material called lithium disilicate. These crowns offer both exceptional strength and natural aesthetics, making them ideal for patients looking for a durable yet aesthetically pleasing restoration.
Benefits of Dental Crowns
Restores Function: Crowns help restore normal chewing and biting functions by covering damaged or weakened teeth.
Improved Appearance: With custom dental restorations from Vijay Dental Miyapur, your crown will blend naturally with your existing teeth, enhancing the overall look of your smile.
Long-Lasting: Crowns are designed to be durable, with materials like metal or zirconia offering extended longevity for your restored tooth.
Protects Teeth: Crowns provide added protection for teeth that are weakened by decay or damage, preventing further deterioration or fracture.
Quick Solution: The process of placing a crown is quick, with results that improve both the functionality and appearance of your teeth in a short period.
Who Should Opt For Dental Crown?
Dental crowns are opted in the following situations:
Dental bridges can restore your smile and revives the ability to chew and speak. Most people opt for dental bridges because it maintains the shape of your face and prevents teeth from drifting out of position.
- When the teeth is broken or decayed or hold other parts of a cracked tooth
- Restoring broken tooth that has been severely worn down
- Cover and support a tooth with a large filling
- Hold a dental bridge in place
- Cover misshaped or discolored teeth
- Cover dental implant
- Cosmetic modification
For children, a crown may be used on primary teeth to:
- Save a tooth that has been damaged or decayed
- Protect the teeth at greater risk of tooth decay
- Reduce the frequency of general anesthesia for children
Crowns Are Made Of Various Materials, Of Which Some Of Them Are Listed Below:
Porcelain Bonded To Precious Metal
Most crowns are made of this material. A precious metal base is made and porcelain is applied in layers over it.
Porcelain
The crowns are made up of porcelain and are not as strong as bonded crowns. They look very natural ad most often used for front teeth
All-ceremic
This type of crown is suitable for all areas of the mouth. It is a metal-free alternative, which can add strength as of a bonded crown.
Glass
These crowns are very natural and can be used anywhere in the mouth
Gold-alloy crowns
It is one of the oldest filling materials. It is used with other metal alloys to increase the strength, making it very hardwearing. These crowns are silver, gold in color.
Generally, you will need to have 2 visits. During the first visit, your dental team will prepare the tooth, take impression and fit the temporary crown. During the second visit, your dentist will fit the permanent crown.
Interested to know more about dental crowns? Get in touch with us right away to know the complete info.
Obturators
Obturators
An obturator is a custom-made dental appliance designed to close an opening in the oral or nasal cavity, typically following the loss of part or all of the palate due to injury, surgery, or congenital conditions. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we offer specialized prosthodontics in Miyapur, creating custom dental restorations like obturators that help restore function and appearance for patients with unique needs.
Types of Obturators
1. Palatal Obturator:
A palatal obturator is designed to cover defects in the roof of the mouth (palate) caused by surgery, injury, or congenital conditions such as cleft palate. It helps seal the oral and nasal cavities, improving speech, swallowing, and preventing food or liquid from entering the nasal cavity.
2. Partial Obturator:
A partial obturator is used when a smaller portion of the palate or oral cavity is missing. This type is often designed for individuals who have lost part of the palate or a portion of the teeth, helping restore normal oral function and appearance while ensuring comfort.
3. Full Obturator:
A full obturator covers the entire palate or oral defect and is typically used when a larger portion of the mouth has been lost. It helps fully restore normal speech, eating, and breathing functions.
4. Immediate Obturator:
An immediate obturator is used right after surgery, often for patients who undergo maxillofacial surgery. It is designed to cover the surgical site and assist in immediate healing, protecting the area from infection and improving comfort.
Benefits of Obturators
Restores Function: Obturators help improve essential functions such as speech, chewing, and swallowing, making everyday activities more comfortable for individuals with oral or palatal defects.
Improves Aesthetic Appearance: With a custom dental restoration to match the natural palate, obturators can restore a natural appearance, boosting confidence and helping patients feel more comfortable in social situations.
Prevents Further Health Complications: By covering oral defects, obturators protect the surgical site or open cavity, preventing food and bacteria from entering and promoting better oral hygiene.
Comfortable and Customizable: Obturators are designed to fit each patient’s unique oral anatomy, providing a comfortable and secure fit for easier speech and eating.
Obturator Functions
The following are a few functions of the Obturator:
- An obturator can be used to keep the wound clean and it can enhance the healing of traumatic or post surgical defects
- It can also help to reshape or reconstruct the defect
- In some scenarios, it makes speech possible
- It can also be used to correct lip and cheek position
- In the case of deglutition and mastication impairs, it can be used to improve functions
- It decreases the flow of exudates in the mouth
Objectives Of Obturator
- It should be comfortable
- Should be able to restore speech, deglutition and mastication
- Should be acceptable cosmetically
- To achieve all these objectives, the Obturator should have enough support, retention and stability
Objectives Of Obturator
Obturators are classified into three types: surgical, Interim, and definitive. The placement of a surgical obturator involves a surgical process, and this obturator is designed to replace the missing structural components, including the plates and associative dentoalveolar structures of the maxillary arch.
The Interim Obturator acts as an alternative to the Surgical Obturator after the initial healing period in the postoperative period is completed. During this phase, multiple adjustments are made to the prosthesis. Teeth are frequently added to enhance the mouth’s functionality and support nutritional intake.
The definitive obturator involves replacing functional teeth to maximize oral functioning capacity. This phase can develop the appearance and aesthetic structure.
Eye Prosthesis (Ocular Prothesis)
Eye Prosthesis (Ocular Prothesis)
An eye prosthesis, also known as an ocular prosthesis, is a custom-made artificial eye designed to replace a missing or damaged eye due to injury, illness, or congenital conditions. At Vijay Dental Miyapur, we offer advanced prosthodontics in Miyapur services, creating custom dental restorations such as ocular prostheses to help patients regain both appearance and comfort. Our prosthetic eyes are designed to not only look natural but also restore confidence and enhance the overall quality of life.
Types of Eye Prosthesis
1. Custom Ocular Prosthesis:
A custom ocular prosthesis is individually crafted to match the unique shape, size, and color of the patient’s natural eye. It is made from high-quality materials such as acrylic or glass and is designed to fit securely in the eye socket, providing a realistic appearance.
2. Stock Ocular Prosthesis:
A stock ocular prosthesis is a pre-made prosthetic eye available in standard sizes. It can be a temporary solution for patients who need immediate eye replacement before a custom prosthesis is made. While it is more affordable, the fit and appearance are not as personalized as custom prostheses.
3. Implant-Supported Ocular Prosthesis:
An implant-supported ocular prosthesis is a permanent solution for patients who have undergone eye removal (enucleation). In this case, a small titanium implant is placed in the eye socket, which integrates with the bone and provides support for a prosthetic eye. This type of prosthesis offers enhanced stability, comfort, and a more natural appearance.
4. Scleral Shell Prosthesis:
A scleral shell prosthesis is designed for patients who still have the existing eye but may have a damaged or malformed eye. It fits over the existing eye and covers the damaged tissue, providing a natural appearance without the need for enucleation.
Benefits of Eye Prosthesis
Restores Aesthetic Appearance: A custom ocular prosthesis enhances facial symmetry, helping to restore the natural appearance of the face, especially when an eye has been lost due to trauma or illness.
Boosts Confidence and Self-Esteem: Replacing a missing eye can significantly improve the patient’s self-image and help them regain confidence in social interactions.
Improved Comfort: With a well-fitting ocular prosthesis, patients can experience greater comfort in daily activities, including eating, speaking, and engaging in physical activities.
Enhanced Functionality: Implant-supported and custom ocular prostheses can help maintain the functionality of the eye socket, preventing further complications and maintaining the overall health of the surrounding tissues.
Durability: Eye prostheses are designed to be durable, long-lasting, and easy to maintain with proper care, ensuring that patients can continue to enjoy a natural look for years.
Surgery Types
The surgery is categorized into two types. Depending on the type of surgery, the type of prosthetic eye will vary:
Evisceration
In this method, the jelly-like inside of the eye is suctioned out. This is performed by making an incision in the front of the eye. However, the procedure preserves tissues in the outer eye, and eye socket.

Ocular Prothesis
In this method, the eye is cut away and removed from the eye socket. Depending on the type of eye condition and degree of eye damage, your doctor will decide on the type of method.
Who Should Go For Prosthetic Eye?
Prosthetic eye can enhance the appearance of the affected eye socket. Most people prefer wearing an eye patch or bandage. In people who lost the entire eye, an ocular implant and prosthesis prevent the tissues in the eye socket from growing to fill the empty space.
